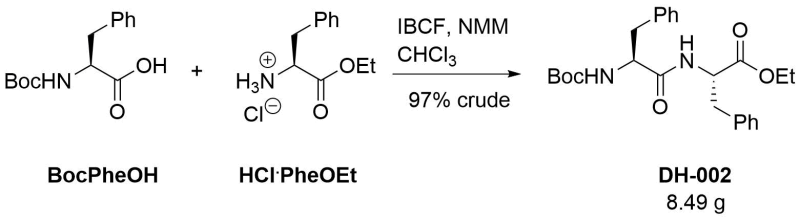
Coupling of Boc-phenylalanine with phenylalanine ethyl ester hydrochloride
SyntheticPage 921
Submitted: April 27, 2020, published: April 29, 2020
Authors
Bart Dietrich (bart.dietrich@glasgow.ac.uk)
A contribution from
Chemicals
L-Phenylalanine ethyl ester hydrochloride (Fluorochem)
Isobutyl chloroformate (Fluorochem)
N-Methylmorpholine (TCI)
Chloroform (HPLC grade)
Procedure
Author Comments
- No special precautions with regards to anhydrous conditions or inert atmosphere are required on this scale.
- Carrying out the reaction at ice/water temperature reduces the formation of a pink-coloured impurity somewhat although the gains are minimal.
- The crude compound may be used in the next step without purification as impurities tend to wash out in the workup of the next step.
Data
dH (500 MHz, DMSO-d6, 25 °C) 8.38 (0.2H, d, J 6.75, Rot-1 NHCH*CO2Et), 8.32 (0.8H, d, J 7.50, Rot-2 NHCH*CO2Et), 7.30-7.16 (10H, m, HAr), 6.85 (0.8H, d, J 8.80, Rot-2 NHBoc), 6.41 (0.2H, d, J 8.50, Rot-1 NHBoc), 4.47 (1H, dd, J 14.33, 7.73, CH*NHBoc), 4.18 (0.8H, td, J 9.65, 4.00, Rot-2 CH*CO2Et), approx. 4.08-4.02 (0.2H, Rot-1 CH*CO2Et), 4.03 (2H, q, J 7.10, CH2CH3), 3.05-2.95 (2H, m, PhCaH2), 2.89 (1H, dd, J 13.80, 3.95, PhCbHaHb), 2.67 (1H, dd, J 13.73, 10.68, PhCbHaHb), 1.28 (7.2H, s, Rot-2 C(CH3)3), 1.14 (1.8H, s, Rot-1 C(CH3)3), 1.09 (3H, t, J 7.10, CH2CH3).
dH (500 MHz, DMSO-d6, 80 °C) 7.95 (1H, d, J 7.30, NHCH*CO2Et), 7.29-7.16 (10H, m, HAr), 6.39 (1H, br s, NHBoc), 4.55 (1H, td, J 7.82, 6.33, CH*NHBoc), 4.22 (1H, td, J 9.08, 4.70, CH*CO2Et), 4.07 (2H, q, J 7.09, CH2CH3), 3.09-2.93 (3H, m, PhCH2), 2.74 (1H, dd, J 13.95, 9.55, PhCH2), 1.30 (9H, s, C(CH3)3), 1.14 (3H, t, J 7.10, CH2CH3).
dC (100 MHz, DMSO-d6, 25 °C) 171.79, 171.25, and 155.07 (C=O), 138.03, 136.96, 129.12 (broad, likely two overlapping peaks), 128.20, 127.93, 126.52, and 126.12 (CAr), 77.96 (C(CH3)3), 60.47 (CH2CH3), 55.44 (CH*CO2Et), 53.54 (CH*NHBoc), 37.41 (PhCbH2), 36.75 (PhCaH2), 28.08 (Rot-2 C(CH3)3), 27.73 (Rot-1 C(CH3)3), 13.88 (CH2CH3).
dC (125 MHz, DMSO-d6, 80 °C) 170.97, 170.57, and 154.40 (C=O), 137.47, 136.59, 128.64, 128.60, 127.69, 127.46, 126.00, 125.64 (CAr), 77.82 (C(CH3)3), 60.03 (CH2CH3), 55.29 (CH*CO2Et), 53.04 (CH*NHBoc), 37.30 (PhCbH2), 36.68 (PhCaH2), 27.66 (C(CH3)3), 13.36 (CH2CH3).
HRMS (ESI) m/z: [M+Na]+ calcd for C25H32N2NaO5 463.2203; found 463.2190.
Supplementary Information
Keywords
amide coupling, amides, amino acids, peptides