Wittig- Horner Reaction of Triethyl phosphonoacetate with Formaldehyde in Aqueous Medium
SyntheticPage 799
DOI:
Submitted: September 19, 2015, published: September 21, 2015
Authors
RAJU THOMBAL (rthombal@gmail.com)
A contribution from
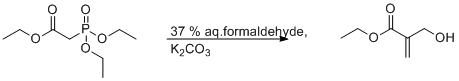
Chemicals
1) triethyl phosphonoacetate
2) 37% aq. Formaldehyde
3) potassium carbonate
Procedure
A mixture of triethyl phosphonoacetate (22.4 g, 0.1 mol) and a 37% aqueous solution of formaldehyde (32.4 g, 0.4 mol) were stirred at room temperature. A saturated solution of potassium carbonate (24.15 g, 0.175 mol) was added to the above mixture over 30 min. After addition, the reaction mixture reached 30 – 35 0C. Stirring was continued for an additional 2 h. The reaction was quenched with a saturated solution of ammonium chloride (35 mL). The reaction mixture was then extracted with ethyl ether (3x 12.5 mL). Organic layers were combined and dried over sodium sulfate. The solvent was evaporated using a rotary evaporator, and the product (colourless oil) was purified using flash chromatography using 20% ethyl acetate/hexanes. This purification yielded the pure product as colourless oil (8 g, 70%).
Author Comments
2) Slow addition of saturated potassium carbonate is required.
Data
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 6.24 (s, 1H), 5.82 (s, 1H), 4.3 (s, 2H), 4.24-4.19 (m, 2H), 2.72 (bs, 1H), 1.3 (t, J=7.3Hz, 3H)
13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 166.2, 139.6, 125.3, 62.2, 60.7, 14.0.
Lead Reference
Keywords
addition, alcohols, alkenes, elimination, esters, organo phosphorous