Addition of diethyl malonate to reactive intermediate (iminoketene) of anthranilic acid.
SyntheticPage 689
DOI:
Submitted: August 7, 2013, published: August 29, 2013
Authors
Parshant Singh (parshantmanhas@yahoo.com)
Sourav Kalra (sourav.niper@gmail.com)
Chemicals
Anthranillic acid (reagent grade, > 98%, Sigma aldrich)
Thionyl chloride (reagent grade, 97%, Sigma aldrich)
Benzene
Diethyl malonate (synthesis grade, Merck millipore)
Thionyl chloride (reagent grade, 97%, Sigma aldrich)
Benzene
Diethyl malonate (synthesis grade, Merck millipore)
Procedure
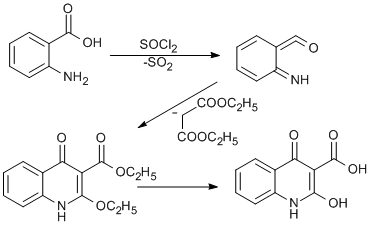
Anthranillic acid (1 g, 7.3 mmol, 1.0 eq) was dissolved in dry benzene (20 ml) in a round bottomed flask and thionyl chloride (0.6 ml, 5.2 mmol) was added dropwise to the anthranillic acid under an inert atmosphere. The mixture was refluxed for 30 minutes at ambient temperature. This led to the formation of iminoketene (6-iminocyclohexa-2,4 dienylidene) methanone. Diethyl malonate 1.2 ml (1.1 mmol) was then added to the round bottom flask. The iminoketene (6-iminocyclohexa-2,4 dienylidene)methanone formed reacts with diethyl malonate to the form ethyl 2-ethoxy-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylate. The compound formed was then hydrolysed under reflux with 20ml of 10% dilute hydrochloric acid to produce ethanol and 2-hydroxy- 4-quinolone-3-carboxylic acid, which was crystallized with ethanol to form white coloured crystals (1.23 g, 82.3 % yield).
Author Comments
- Thionyl chloride is a reactive compound that can violently and/or explosively release dangerous gases upon contact with water and other reagents. So care should be taken when handling such reagents.
- The iminokete formed cannot be isolated at room temperature and is stable above 60oC.
- This reaction has been performed with substituted anthranillic acid and provides good yields for the drugs with 4-quinolone-3-carboxylic acid nucleus but for certain cases it is difficult to get higher yields
- Solvents such as benzene are carcinogenic in nature, so these solvents should be handled with intense care
Data
1H NMR (293K, DMSO) 7.58 (d, 1H, C-5), 6.92 (t, 1H, C-6), 7.48 (t, 1H, C-7), 7.00 (d, 1H, C-8), 10.51 (s, enol H), 11.42(s, NH)
Lead Reference
T. Kametani, T. Higa, M. Koizumi, M. Ihara, K. Fukumoto, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1977, 99, 2306 DOI: 10.1021/ja00449a047
Other References
J.K. Son, S. Kim, Y Jahng, Heterocycles, 2001, 55, 1981 DOI: 10.3987/COM-01-9307
Keywords
addition, carboxylic acids, elimination, heterocyclic compounds, hydrolysis, nucleophilic