Transfer hydrogenation of benzpthalide with limonene/palladium on carbon
SyntheticPage 535
DOI:
Submitted: February 8, 2012, published: February 8, 2012
Authors
Ramesha Ramakrishna (ramesha63@hotmail.com)
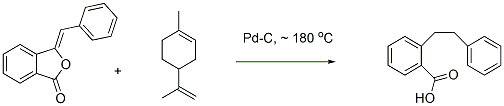
Chemicals
Benzpthalide, purity Min 98% bright yellow solid
Limonene (racemic, known as dipentene) commercial grade
10% Pd-C purchased from ArroraMathey, Culcutta, India
Acetone, commercial Grade
Procedure
Author Comments
The reaction should be carried out under nitrogen atmosphere.
The side product in the process is para methyl iso propyl benzene. 2-(2-phenylethyl)benzoic acid is sparingly soluble in para methyl iso propyl benzene and therefore product crystalizes out.
Mechanical stirring should be started once inside temperature reaches about 100 degree centigrade.
Data
White solid. Mp 130 – 132 oC , .
IR (KBr): 1685, 3155 cm-1 ,1H NMR (200 MHz, CDCl3): δ 2.94 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 3.35 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.15 – 7.51(m, 8H), 8.09(d, J = 9.0 Hz, 1H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 37.6, 38.6, 126.4, 126.7, 128.6, 128.8, 129.0,132.0, 132.3, 133.5, 142.4, 145.3, 173.9.
Lead Reference
A. R. Ramesha, Anjan K. Roy, Synthetic Communications, 2001, 31(16), 2419–2422
Keywords
alkenes, aromatics/arenes, carboxylic acids, hydrogenation, Palladium on carbon, reduction, Transfer hydrogenation