Action of hydrazine hydrate on N-cyano-N1-cyclohexyl-S-methylisothiourea
SyntheticPage 475
DOI:
Submitted: December 21, 2010, published: May 3, 2011
Authors
John Davidson (jsdcrosslaw@tiscali.co.uk)
A contribution from
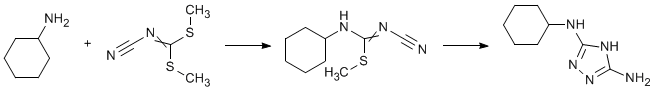
Chemicals
dimethylcyanamidodithiocarbonate
ethanol
cyclohexylamine
hydrazine hydrate
Procedure
Cyclohexylamine (4 g, 0.04 mole) was added to a solution of dimethylcyanamidodithiocarbonate (5 g) in ethanol. On cooling [ice bath], N-cyano-N1-cyclohexyl-S-methylisothiourea separated (5.77 g, 73%). The isothiourea (3.9 g, 0.02 mole) was dissolved in ethanol and hydrazine hydrate (5 ml) and the mixture heated under reflux for 3 h. Water was added. The ethanol was boiled off and the solution was cooled [ice bath] to afford the triazole (2.2 g, 61%).
Author Comments
All chemical manipulations were performed in a fume hood.
Data
N-cyano-N1-cyclohexyl-S-methylisothiourea mp 152-153° (from ethanol)
Found: C 54.5%, H 7.64%, N 21.3%, S 16.0%. C9H15N3S requires: C 54.7%, H 7.66%, N 21.3%, S 16.3%.
3-amino-5-cyclohexyl-[1, 2, 4]-triazole mp 145-146° (from hot water)
Found: C 52.7%, H 8.7%, N 38.7%. C8H15N5 requires C 53.0%, H 8.3%, N 38.6%
Lead Reference
J. S. Davidson, Chem. & Ind., 1965, 1077-1078
Other References
J. S. Davidson, J. Chem. Soc. (C), 1969,194-195
Keywords
addition, amines, condensation reaction, heterocyclic compounds, nucleophilic, substitution, triazole