Formation of benzyl azide from benzyl bromide
SyntheticPage 408
DOI:
Submitted: May 6, 2010, published: May 6, 2010
Authors
Peter Scott (peter.scott@warwick.ac.uk)
Suzanne Elizabeth Howson (s.e.howson@warwick.ac.uk)
A contribution from
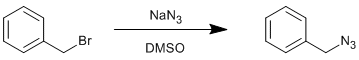
Chemicals
Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO)
Sodium azide
Water (distilled)
Diethyl ether
Sodium sulfate
Procedure
Benzyl bromide (2.0 ml, 16.84 mmol, 1.0 eq.) was dissolved in DMSO (40 ml). Sodium azide (1.64 g, 25.26 mmol, 1.5 eq.) was added as a solid and the reaction was stirred overnight at ambient temperature. Water (75 ml) was added slowly (exothermic) before extracting the product into diethyl ether (3 × 150 ml). The combined diethyl ether layers were washed with brine (2 × 150 ml), dried over sodium sulfate and the solvent removed to leave a clear oil. Yield = 1.63 g, 12.24 mmol, 73%.
Data
1H NMR (400 MHz, 298 K, CDCl3) 7.42-7.32 (5H, m, Ph), 4.35 (2H, s, CH2).
13C{1H} NMR (100 MHz, 298 K, CDCl3) 135.4 (Ph), 128.9 (Ph), 128.3 (Ph), 128.2 (Ph), 54.8 (CH2).
MS (EI/CI) m/z 105.1 [M-2N]+.
IR cm-1: 2090 s, 1497 w, 1455 m, 1253 m, 876 w, 735 m, 696 s.
Elemental Analysis found (Calculated for C7H7N3) % C 63.53 (63.14), H 5.72 (5.30), N 31.34 (31.56).
Lead Reference
Keywords
alkyl/alkenyl/aryl halides, Azide, nucleophilic, substitution